Diet Chart for Diabetic Patient
What is the Diet Chart for Diabetic Patients?
Diet – a term carrying a lot of misconceptions. To some diets means starving themselves while to some diets is only for weight loss. However, the true meaning of diet is much more diverse and helps people make more informed choices for overall well-being. To help maintain good health a diet chart is a guide that lists foods along with their nutritional value. A diet chart is a guide that lists foods and their nutritional value in order to support good health. It is an organized plan that advises on the type, quantities, and timing of food & beverages to be consumed to meet the body’s nutritional requirements.
There is no ‘one size fits all’ approach when it comes to diet. A diet plan is customised based on its intended use/goal. Although there are generic diet charts, a customised chart is essential for effectively reaching the goal. Everybody is different and so are the nutritional requirements, thus a tailored diet chart seeks to cater to the body’s requirements specifically.
Just as diet plans vary based on the objectives/goals they also vary based on the underlying medical condition. Patients with diabetes have different diet plans. The body’s inability to produce enough insulin or use it efficiently is the cause of this chronic illness. Diet chart for diabetic patients focuses on promoting eating a variety of foods providing adequate nutrients while limiting carbohydrate intake which has an impact on blood sugar levels. These diet charts emphasize guiding people with diabetes in controlling their blood sugar levels through healthy eating.
Table of Contents
Foods that a Person with Diabetes should Avoid
Diabetes is a chronic condition that requires maintaining the blood sugar level within a healthy range. When we consume food, it is broken down into glucose (sugar) in the digestive tract, further, the pancreas produces insulin to help regulate this glucose (sugar) into the body’s cells and used as energy. However diabetic patients have a harder time controlling their blood sugar levels after eating because their insulin production is either not adequate or ineffectively used. For this reason food intake is crucial for diabetic patients as the foods they eat have a direct impact on blood glucose levels. There are certain foods that a person with diabetes should avoid including,
| Category | Food Products |
| Refined & Processed Carbohydrates | White bread, white rice, pasts, instant noodles |
| Sugary Food & Drinks | Fruit juices, candies, cookies, cakes, sweetened teas |
| Unhealthy Fats | Fried foods, high fat meats & trans fats |
| High Sugar Fruits | Fruits like mangoes, grapes, pineapple, etc, should be consumed in moderation |
Foods to be included in your Diabetic Diet
It’s critical for diabetic patients to make informed dietary choices and monitor their intake in order to maintain their blood sugar levels. The foods that are part of the diabetic diet help keep blood sugar levels steady, support general health and lower the risk of complications from diabetes including kidney issues, nerve damage, heart disease, and other related disorders. In addition to assisting with blood sugar regulation, making healthy food choices promotes long-term health by averting the negative consequences of diabetes.
- High-Fiber Foods: Whole grains, legumes
- Lean Proteins: Fish, tofu, eggs
- Healthy Fats: Nuts, seeds, avocados, olive oil
- Low-Glycemic Fruits: Berries, apples, pears, oranges, kiwi
- Non-Starchy Vegetables: Non-Starchy Vegetables
7-Day Diet Chart for Diabetic Patients
Monday:
- Breakfast: Vegetable oats/milk oats/2-egg whites, 2 whole wheat toasts with grilled vegetables & a cup of tea/coffee.
- Mid-morning: A cup of buttermilk
- Lunch: 2 chapatis with sauteed vegetables, 1 bowl of dal/chicken or curd
- Evening: 1 bowl of sprouts, roasted chana or a bowl of fruits
- Dinner: 2 chapatis with vegetables, salad & a bowl of fish/dal
Tuesday:
- Breakfast: Idli or Poha with vegetables, a cup of tea/coffee or low-fat milk.
- Mid-morning: A small handful of almonds
- Lunch: 1 bowl of millet khichdi, curd, and sauteed vegetables
- Evening: 1 bowl of soup or roasted chana
- Dinner: 1-2 multigrain chapati with mixed vegetables, salad & a bowl of fish/dal
Wednesday:
- Breakfast: Vegetable cutlet or 1 egg with 2 toasts, grilled vegetables, a cup of tea/coffee or milk
- Mid-morning: 1 pear or orange
- Lunch: 1-2 cups of brown rice, salad, 1 bowl of chana/chicken
- Evening: A small portion of roasted makhana
- Dinner: 1-2 jowar roti, mixed vegetables, salad & a bowl of dal.
Thursday:
- Breakfast: Multigrain bread sandwich with vegetables or vegetable dalia
- Mid-morning: 1 apple/orange or roasted chana
- Lunch: 1-2 multigrain roti, 1 bowl of kidney beans/chicken & a bowl of salad
- Evening: A cup of unsweetened green tea, 2 egg whites
- Dinner: 2 besan chilla or oats with vegetables, 1 bowl of fish/dal & salad
Friday:
- Breakfast:1 bowl of poha with vegetables, 1 cup curd, a handful of nuts
- Mid-morning: 1 bowl of sugar-free fruit custard
- Lunch: 2 chapatis, vegetables, salad & 1 bowl of sprout
- Evening: 1 bowl of sprouts or bhel puri
- Dinner: Chicken/mixed vegetables with 1 small portion of brown rice & salad
Saturday:
- Breakfast: Besan cheela with a small bowl of curd & a cup of tea/coffee or milk
- Mid-morning: A handful of mixed nuts
- Lunch: 2 chapatis, mixed vegetables, paneer/chicken salad & 1 bowl of curd
- Evening: Roasted chana or 1 apple
- Dinner: A bowl of fish/dal, 2 chapatis, mixed vegetables & salad
Sunday:
- Breakfast: Ragi dosa or 2 medium Idli with sambar & a cup of tea/coffee or milk
- Mid-morning: A small handful of roasted makhana
- Lunch: Vegetable dalia with a side of curd or 2 multigrain roti, dal, mixed vegetables & a bowl of curd
- Evening: Roasted chana or 1 bowl of sprouts
- Dinner: Grilled fish/palak paneer & a small portion of brown rice with salad.
Role of Diet Management in Controlling Diabetes
Diet plays a key role in managing blood sugar levels, supports weight management and reduces the complications associated with diabetes. An ideal diet plan for controlling diabetes includes all the macronutrient and micronutrient components and covers all food groups to ensure the body receives enough nutrition with controlled carbohydrates. There are other factors that help with diet management including:
- Portion Control: Refers to eating small quantities & maintaining a balance of carbs, proteins & fats.
- Meal Timing: Involves at consistent times throughout the day, preventing extreme sugar fluctuations.
- Staying Hydrated: Supports kidney function & helps flush out excess sugar
Factors Affecting Diet Chart for Diabetic Patients in India
Various factors affect diet charts for diabetic patients in India including,
| Factors | Description |
| Cultural Preferences | Regional food habits like rice, wheat, or millet-based diets |
| Age & Gender | Nutritional needs vary for children, adults & elderly, as well as between genders |
| Health Condition | Pre-existing issues like hypertension, heart disease, etc, influence food choices |
| Weight Management | Calorie deficit for reducing fat, common among Indians |
| Lifestyle | Diet depends on activity levels, like sedentary office jobs or physical labour |
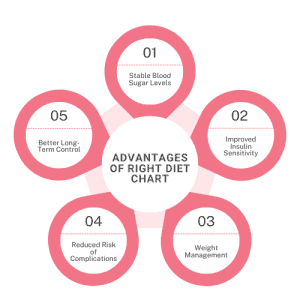
Advantages of Right Diet Chart on Diabetes Management
Conclusion
For diabetic patients, a carefully thought-out diet plan is essential to controlling blood sugar levels and maintaining overall health. Patients with diabetes should follow a diet that emphasises well-balanced meals that include the appropriate amounts of fats, proteins, carbs, and other nutrients. Maintaining stable energy levels and improving insulin sensitivity can be achieved by adhering to a customised diet. Under the direction of a nutritionist or specialist a customised diet plan is created with the patient’s overall health in mind. It aids in the efficient management of diabetes and fosters long-term health.
FAQs Around Diabetic Patient
Tips to have better control of your blood sugar levels?
A combination of strategies including adhering to a diabetic-specific diet plan, exercising, drinking plenty of water etc. can help control blood sugar levels.
Can people with diabetes eat rice?
Diabetic patients can eat rice as a part of their diet however it should be consumed in moderation and small portions.
Can diabetic patients eat dates?
Dates are low on glycemic index (GI) and release sugar slowly into the blood. Dates can be consumed by diabetic patients in moderation.
Which fruit is good for diabetic patients?
Fruits with low to moderate glycemic index (GI), which release sugar slowly into the blood are recommended for diabetic patients apples, bears, berries, etc.


