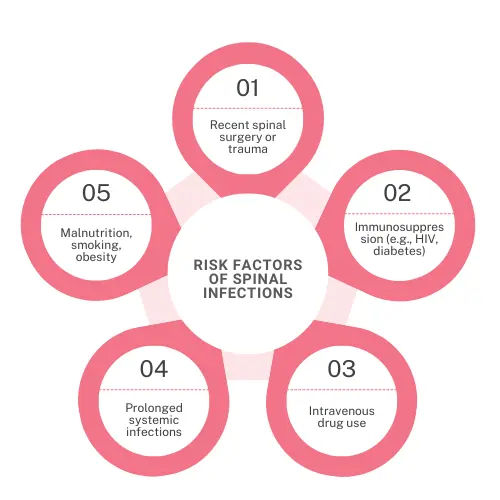
We have all experienced it - ‘infections’ ranging from the most prevalent ones like viral fever to more uncommon ones like spinal infections. Many people in India are affected with a variety of infections. One such uncommon but potentially dangerous condition is a spinal infection brought on by bacteria or fungi. Traumatic injuries to the spine, previous spine surgery or secondary infections that arise elsewhere in the body are all linked to spinal infections. Both the spinal cord and the vertebrae may be impacted by spinal infections. If left untreated spinal infections can become life-threatening and lead to complications like spinal cord stroke, severe to permanent nerve loss, paralysis, etc.
Other symptoms of spinal infections include reduction in mobility, weakness, loss of bowel function, problems urinating, etc.